Vacuum Blocks (Liquidity Gaps) in ICT trading refer to gaps formed during high market volatility, often caused by major economic news releases, geopolitical events, supply anddemand imbalances, or the opening of new trading sessions.
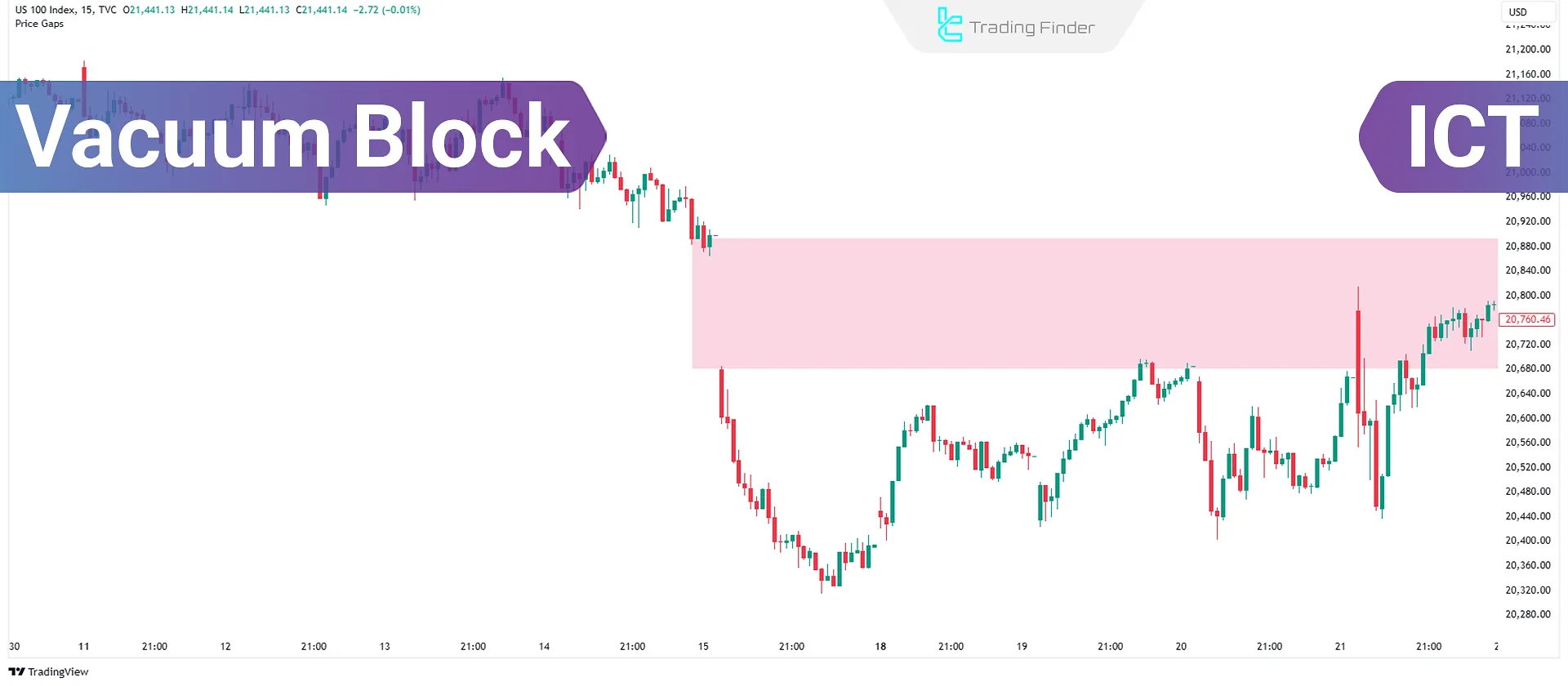
What is a Vacuum Block?
A Vacuum Block is a gap in price action that occurs due to major economic events (e.g., FOMC, NFP), the opening of the market, or the start of a new session.
Since no trades take place in these gaps, they are known as liquidity voids. Price typically returns to fill this gap before continuing in the original direction.
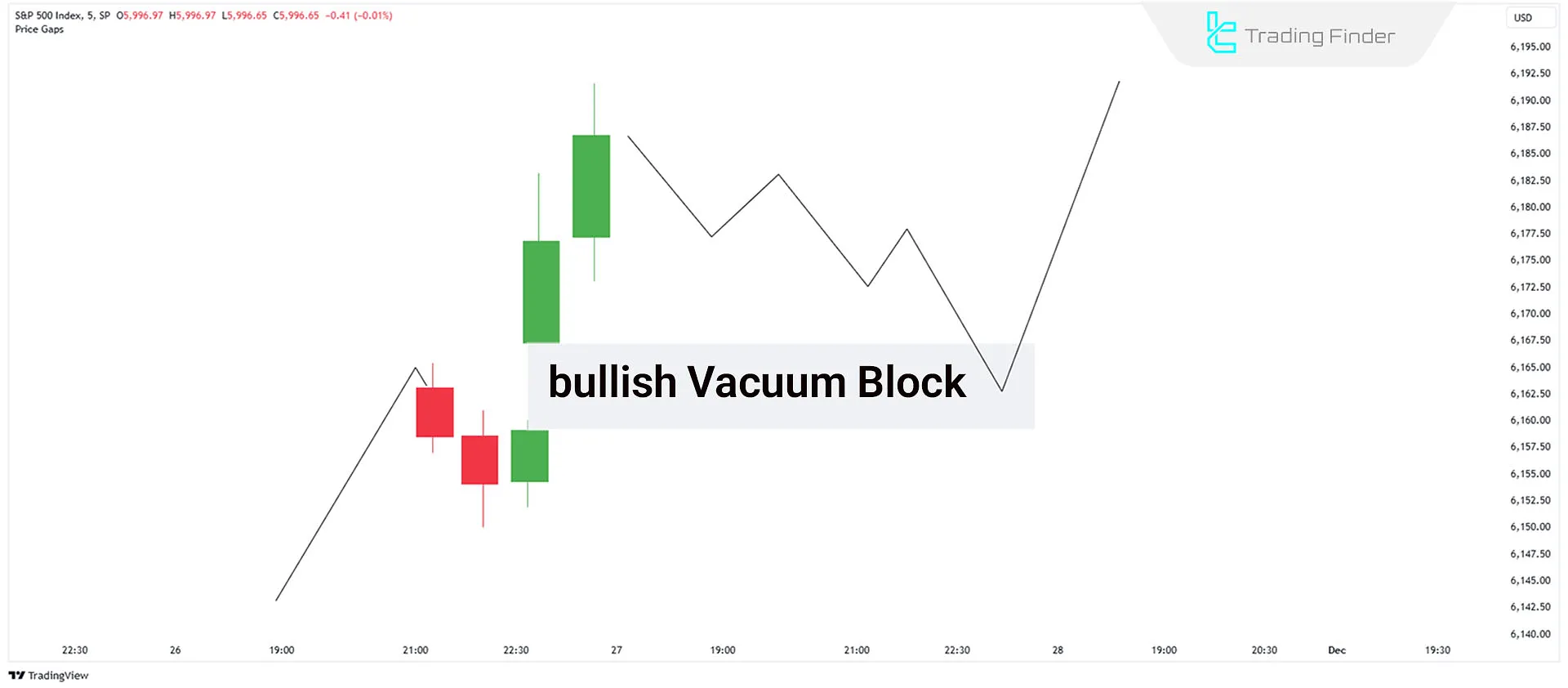
Formation of a Bullish Vacuum Block
A Bullish Vacuum Block forms when price gaps up above the current market level, creating a price gap.
This scenario indicates strong bullish momentum but also a liquidity void that price is likely to revisit. Price tends to return to this area to fill the liquidity gap before resuming its upward movement.
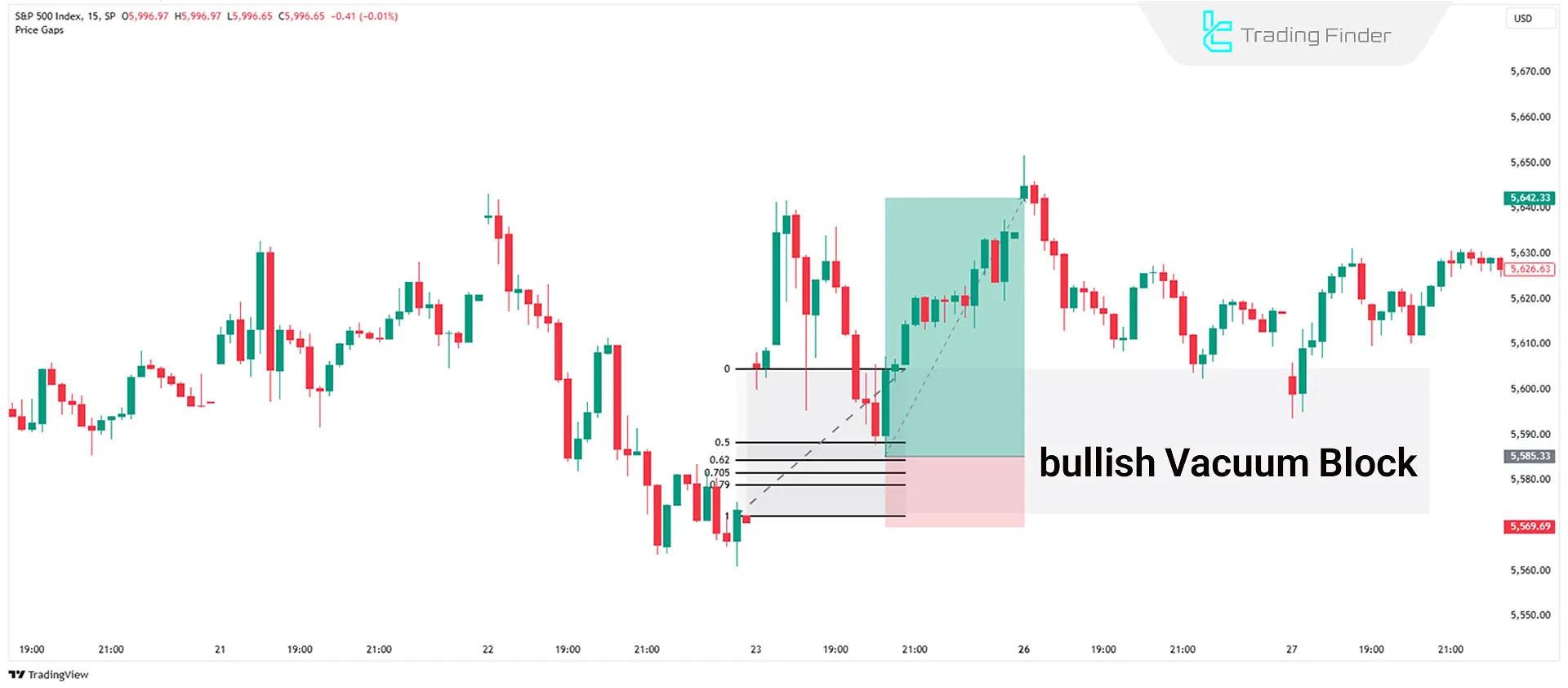
How to Trade a Bullish Vacuum Block?
To trade a Bullish Vacuum Block, first analyze the cause and impact of the event that led to the price gap. If the event has a long-term impact, wait for price to return to the vacuum block before looking for trade confirmations.
- Once price retraces to the gap, look for bullish confirmation signals, such as a Market Structure Shift (MSS) on lower timeframes or confluence with OTE levels.
- After confirmation, enter a buy trade and place the stop-loss below the lowest point of the vacuum block.
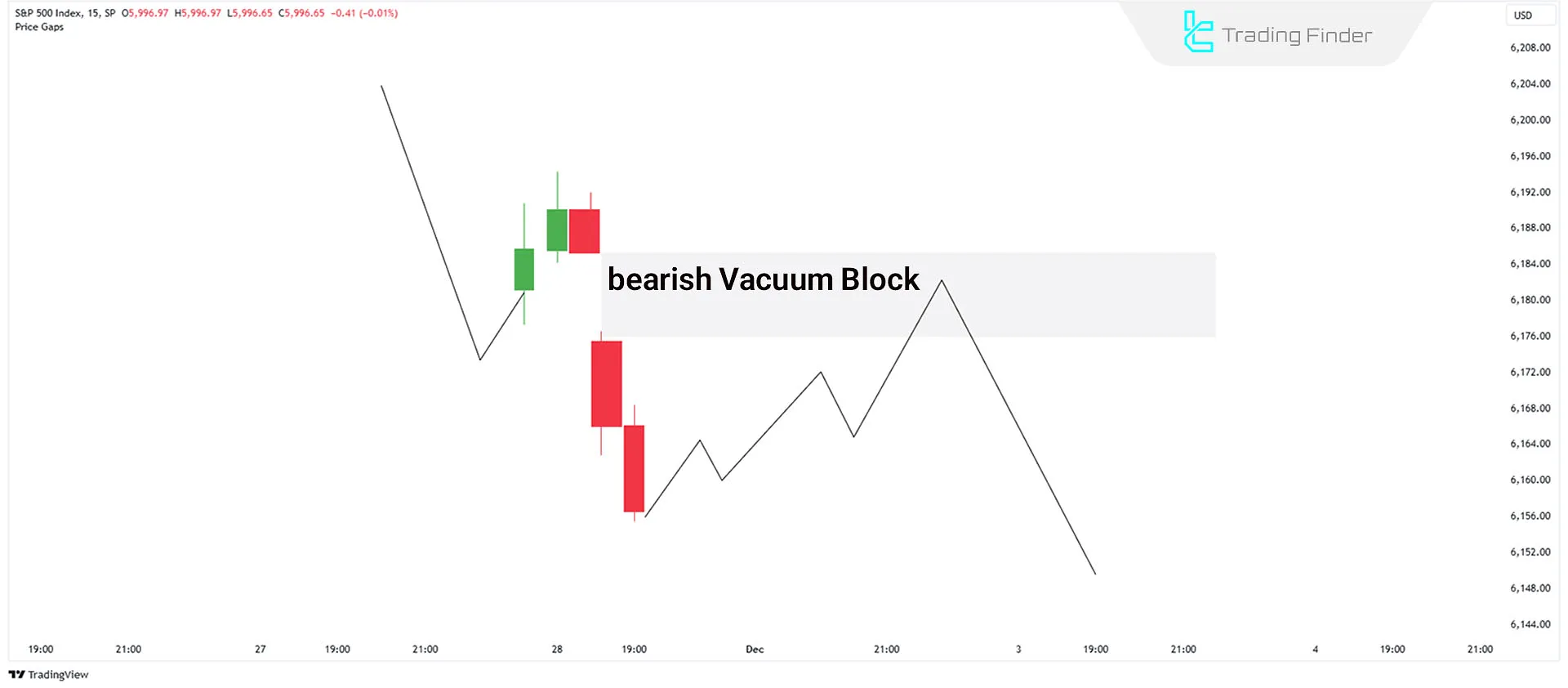
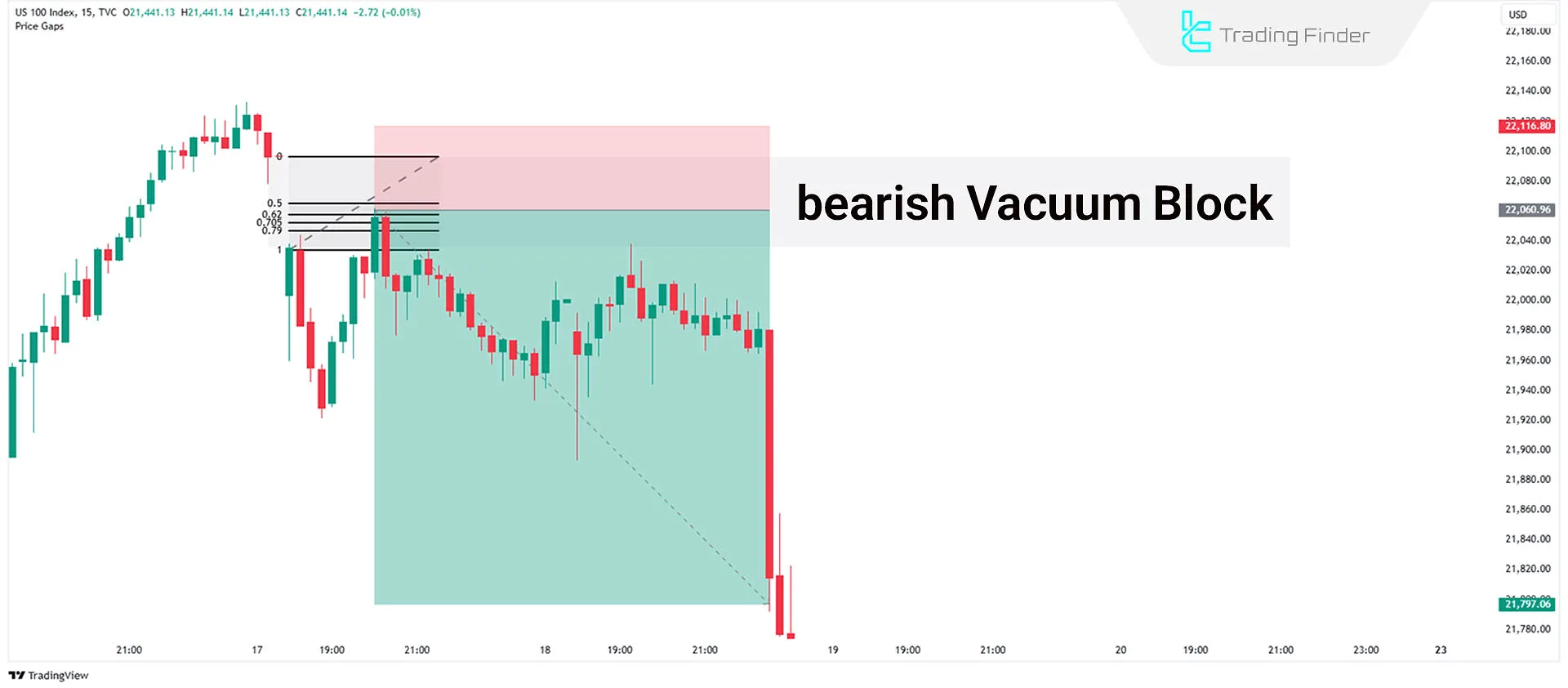
Formation of a Bearish Vacuum Block
A Bearish Vacuum Block forms when price gaps down below the current market level, creating a liquidity void. This often occurs due to major economic or geopolitical events, causing a sharp decline in asset prices.
- A bearish vacuum block indicates strong bearish momentum, but price tends to retest the gap before continuing downward.
How to Trade a Bearish Vacuum Block?
To trade a Bearish Vacuum Block, first identify the cause and significance of the price gap. If the event has a lasting impact, wait for price to return to the liquidity void before looking for trade confirmations.
- Once price retraces to the vacuum block, look for bearish confirmations, such as Market Structure Shift (MSS) on lower timeframes or reaction to OTE levels.
- After confirmation, enter a sell trade and place the stop-loss above the highest point of the vacuum block.
Identifying Vacuum Blocks with Indicators
To simplify Vacuum Block detection, traders can use the [TFlab] free indicator, available on different platforms:
- MT4 Version of the Vacuum Block Indicator
- MT5 Version of the Vacuum Block Indicator
- TradingView Version of the Vacuum Block Indicator
Which Assets Experience Liquidity Voids More Frequently?
Vacuum Blocks typically occur in assets sensitive to economic news and macro events, including:
- Major forex pairs (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/USD)
- Stock indices (e.g., S&P 500, NASDAQ)
- Commodities (e.g., gold, crude oil)
- Cryptocurrencies, which are known for high volatility
Does Price Always Fill a Vacuum Block?
Price does not always fully fill a vacuum block.
- Sometimes, only part of the gap is filled before the trend resumes.
- Other times, price completely fills the gap before continuing in the same direction.
- There is no guarantee that a vacuum block will be filled entirely.
Conclusion
A Vacuum Block (Liquidity Gap) is a price gap caused by high volatility or economic events. These gaps tend to be filled, making them useful for identifying key trading levels and risk management strategies.













