High-frequency trading platforms rely on ultra-low latency infrastructure, FIX API connectivity, and automated execution engines capable of processing thousands of orders per second. Professional HFT traders prioritize sub-50ms execution, co-located servers, and advanced algorithmic systems to capture micro-price inefficiencies across forex, indices, and commodities.
However, even the fastest trading software depends on broker-side performance, pricing models, and regulatory standards. Factors like ECN execution, API access, commission structure, and VPS hosting directly impact strategy efficiency. In the next section, we review the best brokers for high-frequency trading.
 | Pepperstone | |||
 | FP Markets | |||
 | FXCM | |||
| 4 |  | Tickmill | ||
| 5 |  | IC Markets | ||
| 6 |  | FxPro | ||
| 7 |  | XM Group | ||
| 8 |  | Eightcap | ||
| 9 |  | TMGM | ||
| 10 |  | AvaTrade |
HFT Brokers Rated by Trustpilot
Trustpilot ratings provide valuable insight into broker reliability for high-frequency trading. Leading HFT brokers like IC Markets, AvaTrade, and FP Markets hold strong 4.8 out of 5 scores from over 70,000 combined reviews, reflecting high execution quality, platform stability, and overall client satisfaction.
Broker | Trustpilot Rating | Number of Reviews |
IC Markets | 49,951 | |
11,790 | ||
FP Markets | 9,750 | |
FXCM | 818 | |
3,196 | ||
Eightcap | 3,417 | |
TMGM | 833 | |
FxPro | 857 | |
Tickmill | 1,066 | |
2,940 |
High-Frequency Trading Platforms Ranked by Minimum Spreads
Minimum spreads play a critical role in high-frequency trading profitability, where every fraction of a pip impacts performance. Leading platforms like Pepperstone, Swissquote, and AvaTrade offer ultra-tight spreads from 0.0 pips, making them preferred choices for scalping, algorithmic trading, and low-latency strategies.
Broker | Min. Spread |
FP Markets | 0.0 Pips |
Interactive Brokers | 0.0 Pips |
Swissquote | 0.0 pips |
AvaTrade | 0.0 Pips |
0.0 Pips | |
FxPro | 0.0 Pips |
0.0 Pips | |
Pepperstone | 0.0 Pips |
0.2 Pips | |
Saxo | 0.4 Pips |
Non-Trading Fees in HFT Brokers
Non-trading fees directly affect long-term HFT profitability, especially for active algorithmic traders managing multiple accounts. Brokers like IC Markets and FP Markets offer zero deposit and inactivity fees, while others charge up to $50 per year, making cost structure a key factor when selecting high-frequency trading platforms.
Broker | Deposit Fee | Withdrawal Fee | Inactivity Fee |
IC Markets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
$0 | Up to 1% | $0 | |
Tastyfx | $0 | Up to $15 | $0 |
FxPro | $0 | $0 | $5/month |
$0 | $0 | $10/month | |
XM Group | $0 | $0 | $10/month |
$0 | $0 | $10/month | |
IG | 1% charge for Visa and 0.5% charge for MasterCard | $0 | $18/month |
Swissquote | 0.5% for SEPA / 2.9% for non-SEPA or corporate cards | $0 | €15/month |
FXCM | $0 | Up to $40 | $50/year |
High-Frequency Trading Platforms’ Number of Trading Instruments
The number of tradable instruments defines market access for high-frequency trading strategies across forex, stocks, indices, and derivatives. Brokers like Swissquote with over 3 million assets and Saxo offering 71,000 plus instruments provide deep liquidity and diversification, giving HFT traders greater flexibility for multi-asset algorithmic execution.
Broker | Tradable Instruments |
Swissquote | 3M+ |
Saxo | 71,000+ |
IG | 17,000+ |
FXCM | 13,000+ |
2,100+ | |
XM Group | 1,400+ |
AvaTrade | 1,250+ |
Pepperstone | 1,200+ |
Eightcap | 800+ |
Tickmill | 600+ |
Top 8 HFT Forex Brokers
Top HFT Forex brokers combine Tier 1 regulation, low latency execution, and trading conditions built for scalping, EAs, and API based systems. This list covers 8 multi asset brokers, including IC Markets, Pepperstone, FP Markets, and FXCM, with spreads from 0.0 pips, leverage up to 1:1000, and platforms like MT4, MT5, cTrader, and TradingView.
IC Markets
IC Markets is a global multi-asset broker established in 2007, offering access to forex, CFDs, indices, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. With a minimum deposit of $200 and support for 10 base currencies, it serves both retail and professional traders across regulated jurisdictions.

Regulated by ASIC, CySEC, and FSA Seychelles, IC Markets operates under strict financial standards, including fund segregation, external audits, and investor protection up to €20,000 for EU clients. Its multi-entity structure ensures compliance, transparency, and operational stability for global market participants.
For high-frequency trading, IC Markets provides ultra-fast market execution, low-latency infrastructure, and institutional-grade liquidity. Raw Spread accounts on MT4, MT5, and cTrader offer spreads from 0.0 pips with commissions from $3 per lot, making it suitable for scalping, algorithmic trading, and HFT strategies.
The broker supports advanced trading tools, FIX API connectivity, VPS hosting, and Expert Advisors, enabling traders to deploy automated systems efficiently. With average EUR/USD spreads near 0.1 pips, the IC Markets rebate program with up to $3 per lot cashback on Forex pairs, and execution speeds optimized for high-volume trading, the broker remains a preferred choice for systematic traders.
Account Types | Standard, Raw Spread, Islamic |
Regulating Authorities | FSA, CySEC, ASIC |
Minimum Deposit | $200 |
Deposit Methods | Bank Cards, Wire Transfers, Electronic payments, etc. |
Withdrawal Methods | Bank Cards, Wire Transfers, Electronic payments, etc. |
Maximum Leverage | 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Metatrader 4, Metatrader 5, cTrader, cTrader Web, IC Markets Mobile |
IC Markets Pros and Cons
Overall, IC Markets combines low trading costs, strong regulation, and high-performance infrastructure. Below, we outline the main advantages and disadvantages to help traders evaluate whether this broker fits their high-frequency and algorithmic trading needs.
Pros | Cons |
Ultra-low spreads from 0.0 pips on Raw accounts | Limited leverage under ASIC and CySEC regulation |
Strong support for HFT and algorithmic trading | No PAMM account offering |
Regulated by ASIC, CySEC, and FSA | Restricted access in several countries |
Multiple advanced platforms (MT4, MT5, cTrader) | No proprietary trading platform |
FXCM
FXCM, short for Forex Capital Markets, is a long standing Forex and CFD broker founded in 1999. It operates under multiple regulators, including FCA, ASIC, CySEC, FSCA, and ISA. Traders can start with a $50 minimum deposit, trade from 0.01 lot, and access market execution across major asset classes, after completing the FXCM registration process.
Safety features include segregated client accounts under FCA and ASIC frameworks, negative balance protection across entities, and regular audit practices. Eligible UK clients can receive compensation up to £85,000 under FSCS, while CySEC clients may be covered up to €20,000 under ICF, depending on eligibility rules.
For high frequency and algorithmic trading, FXCM supports API friendly workflows via MT4, TradeStation, and TradingView integration, alongside its proprietary Trading Station. Tight pricing starts from 0.2 pips with zero commission on CFDs, which can matter when strategies depend on fast order routing and slippage control.
FXCM offers three primary account paths, including CFD, Active Trader, and Corporate accounts. The Active Trader tier targets high volume traders with potential FXCM rebates and enhanced pricing, but it requires a $25,000 minimum deposit. Maximum leverage can reach 1:1000 based on region and entity rules.
Account Types | CFD account, Active Trader account, Corporate account |
Regulating Authorities | FCA, ASIC, CySEC, ISA, FSCA |
Minimum Deposit | $50 |
Deposit Methods | Visa/MasterCard, Bank wired, Neteller, Skrill |
Withdrawal Methods | Visa/MasterCard, Bank wired, Neteller, Skrill |
Maximum Leverage | 1:1000 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, TradingView, TradeStation |
FXCM Pros and Cons
FXCM combines multi jurisdiction regulation, platform variety, and cost competitive spreads, but non-trading charges and historical compliance events still matter in broker selection. Next, the key advantages and disadvantages are listed so HFT traders can weigh infrastructure, fees, and account suitability.
Pros | Cons |
Multi regulated broker with FCA, ASIC, CySEC, FSCA, and ISA oversight | 2017 CFTC enforcement action and U.S. exit remains a trust consideration |
Platform coverage across MT4, TradingView, TradeStation, and Trading Station | Inactivity fee can apply after 12 months, up to $50 per year |
Spreads from 0.2 pips and no commission on CFDs | Bank wire withdrawals can cost up to $40 |
Active Trader program designed for high volume and systematic traders | Higher tiers may require larger capital, such as $25,000 for Active Trader |
XM Group
XM Group is a global Forex and CFD broker founded in 2009, offering 55+ currency pairs and over 1,200 stock CFDs within a catalog of 1,400+ instruments. It reports 15 million clients and nearly 14 million trades per day, with offices in Cyprus, South Africa, Dubai, and Belize. One of the most attractive services of the broker is the XM Group copy trading.

XM operates through multiple regulated entities, including CySEC, FSCA, DFSA, and FSC Belize, plus additional frameworks in Mauritius and Seychelles. Core protections include segregated client funds, negative balance protection, and a comprehensive XM Group verification process.
For high frequency and automated workflows, XM runs a MetaTrader only environment on MT4 and MT5, with EA support and market or instant execution. The broker advertises guaranteed fills for orders up to 50 lots, which can suit fast execution styles when latency, slippage control, and consistent order handling matter.
Pricing is spread-based, with Ultra Low spreads from 0.6 pips and no commission except on the Shares account. The minimum deposit starts at $5, leverage can reach up to 1:1000 by entity, and trade sizing starts from 0.01 lot, which supports flexible testing for systematic strategies with a feature-rich XM Group dashboard.
Account Types | Standard, Ultra Low, Shares |
Regulating Authorities | FSC Belize, CySEC Cyprus, FSCA South Africa, DFSA Dubai, FSC Mauritius, FSA Seychelles |
Minimum Deposit | $5 |
Deposit Methods | Credit/Debit Cards, Bank Transfers, E-Wallet Payments |
Withdrawal Methods | Credit/Debit Cards, Bank Transfers, E-Wallet Payments |
Maximum Leverage | 1:1000 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, MT5, Mobile App |
XM Group Pros and Cons
XM Group offers broad instrument coverage and very low entry requirements, but cost details like inactivity charges and execution behavior still matter for systematic traders. Next, the main pros and cons are listed so readers can weigh platform limits, fees, and suitability for high-frequency style trading.
Pros | Cons |
Very low minimum deposit at $5 for most accounts | $10 monthly inactivity fee on dormant accounts |
1,400+ CFDs, including 55+ forex pairs and 1,200+ stock CFDs | MetaTrader only, no TradingView, cTrader, or FIX focused stack |
Multiple regulators, including CySEC, FSCA, DFSA, and FSC Belize | Restrictions in several regions, including the US and Canada |
Negative balance protection across retail accounts | Mixed review signals |
AvaTrade
AvaTrade is a globally regulated Forex and CFD broker supervised by the Central Bank of Ireland, ASIC, CySEC, FSCA, and key regional authorities such as the FSA Japan and ADGM FSRA. It follows MiFID II in Europe and keeps client money in segregated accounts for added protection.
AvaTrade runs multiple entities across Ireland, Cyprus, Australia, South Africa, Japan, Israel, the UAE, and BVI. EU clients may be eligible for up to €20,000 compensation under ICF coverage, depending on the regulated branch, while negative balance protection is available across its regulated structure.
For high-frequency style trading, AvaTrade prioritizes stable order handling through instant execution, multi jurisdiction risk controls, and MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 access. Its typical model uses spread-based pricing rather than commissions, so strategy performance depends heavily on spreads, execution consistency, and broker rules.
Traders can start from a $100 minimum deposit, trade from 0.01 lot, and choose Retail, Professional, Islamic, or Demo accounts, after completing the AvaTrade registration process.
AvaTrade supports WebTrader, Mobile App, and AvaOptions, plus copy trading through DupliTrade and AvaSocial, alongside multi asset access across Forex, indices, commodities, stocks, and crypto. AvaTrade deposit and withdrawal methods include credit cards, e-wallets, bank wire, and PayPal.
Account Types | Retail, Professional, Islamic, Demo |
Regulating Authorities | ASIC, CySEC, CBI, FSA, FSCA, MiFID, ADGM, PFSA, ISA |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Credit/Debit Cards, E-Wallets, Bank Wire Transfer, PayPal |
Withdrawal Methods | Credit/Debit Cards, E-Wallets, Bank Wire Transfer, PayPal |
Maximum Leverage | 1:400 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, Mobile App, WebTrader |
AvaTrade Pros & Cons
AvaTrade combines strong regulation, broad platform coverage, accessible entry requirements, and the AvaTrade rebate program for trading cashbacks, but inactivity charges and account structure limits can affect long term suitability.
Next, the main pros and cons are listed so readers can quickly compare AvaTrade against other HFT ready brokers.
Pros | Cons |
Strong regulatory coverage, including CBI, ASIC, CySEC, FSCA, and MiFID II alignment | Inactivity fee can apply after 2 months when the balance is under $2,000, plus a $100 annual admin fee after 12 months |
Multiple trading platforms including MT4, MT5, WebTrader, Mobile App, and AvaOptions | Fixed spread model may be less attractive for some ultra tight spread scalping needs |
Copy trading options via DupliTrade and AvaSocial | Fewer account types than some competitors, depending on the region |
Broad market access with 1,250 plus instruments and 60 plus Forex pairs | Services restricted in several jurisdictions, including the United States and Belgium |
Eightcap
Eightcap is an Australia founded broker established in 2009, offering 1:500 leverage and access to 6 CFD markets, including Forex, indices, commodities, metals, shares, and crypto. Traders can start with a $100 minimum deposit, trade from 0.01 lot, and choose USD, GBP, AUD, EUR, NZD, CAD, or SGD as base currency.
The broker operates under multiple regulators, including ASIC, FCA, and CySEC, alongside SCB for its global entity. Client safety features include segregated funds and negative balance protection, with compensation coverage up to £85,000 under FSCS for FCA clients and up to €20,000 under ICF for CySEC clients.
For high-frequency style execution, Eightcap uses market execution across MT4, MT5, and TradingView, with scalping allowed on all accounts and stop out set at 50%. Raw accounts advertise spreads from 0.0 pips with a round turn cost of $7 per standard lot, which can be relevant for latency sensitive strategies.
Eightcap differentiates its trading stack with three productivity tools, Capitalise.ai for no code automation, FlashTrader for rapid order placement, and an AI-powered economic calendar with 1,000+ macro events, all available after completing the Eightcap registration process. This setup supports systematic workflows and faster decision cycles, especially when managing multiple instruments.
Account Types | Standard, Raw, TradingView, Demo |
Regulating Authorities | ASIC, FCA, CySEC, SCB |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Crypto, e-wallets, credit/debit card, bank transfer, Online Payment Systems |
Withdrawal Methods | Crypto, e-wallets, credit/debit card, bank transfer, Online Payment Systems |
Maximum Leverage | 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, MT5, TradingView |
Eightcap Pros and Cons
The broker blends strong regulation, TradingView integration, the Eightcap rebate program, and automated tools, but platform limits and inactivity rules can impact long term suitability. Next, the main pros and cons are listed so readers can compare execution, costs, and HFT readiness against other brokers.
Pros | Cons |
Regulated by ASIC, FCA, and CySEC with segregated funds and negative balance protection | An inactivity fee can apply after 3 months, up to 10 EUR GBP USD per month |
TradingView integration plus MT4 and MT5 support | Basic educational resources compared to research-heavy brokers |
Raw pricing with spreads from 0.0 pips and scalping allowed | No Islamic account, PAMM, or built-in copy trading options |
Added tools, including Capitalise.ai, FlashTrader, and AI economic calendar | Minimum deposit is $100, which can be higher than some low entry brokers |
Pepperstone
Pepperstone is a global Forex and CFD broker founded in Melbourne in 2010, offering access to 6 asset classes including Forex, indices, commodities, shares, ETFs, and crypto CFDs. Accounts support 10 base currencies, trade sizing from 0.01 lot, and leverage up to 1:500 via selected entities, all available after completing the Pepperstone registration process.

The broker operates under a broad regulatory network, including ASIC, FCA, CySEC, BaFin, DFSA, CMA Kenya, and SCB. Client funds are held in segregated accounts, and negative balance protection applies across entities, with compensation schemes up to £85,000 under FSCS and up to €20,000 under ICF.
For high-frequency trading, Pepperstone provides Razor pricing with spreads from 0.0 pips and a $3.5 per lot per side commission on Forex. Scalping, Expert Advisors, hedging, and news trading are permitted, which aligns with fast execution workflows and systematic strategies that depend on tight pricing.
Pepperstone supports a wide platform stack, including MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView, and proprietary web and mobile platforms. With instant execution, the Pepperstone rebate program, stop out levels as low as 20 percent for professional clients, and no inactivity fees, it is structured for active trading and frequent order routing.
Account Types | Standard, Razor |
Regulating Authorities | ASIC, SCB, FCA, DFSA, CMA, BaFin, CySEC |
Minimum Deposit | $1 |
Deposit Methods | Apple Pay, Google Pay, Visa, Mastercard, Bank transfer, PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, Union Pay, USDT, ZotaPay |
Withdrawal Methods | Apple Pay, Google Pay, Visa, Mastercard, Bank transfer, PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, Union Pay, USDT, ZotaPay |
Maximum Leverage | 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Proprietary Platform, cTrader, Trading View, MetaTrader 4&5 |
Pepperstone Pros and Cons
Pepperstone delivers strong regulation, platform flexibility, and HFT friendly account rules, but leverage limits and feature gaps like no PAMM still matter for some traders. Next, the key pros and cons are listed so readers can compare Pepperstone against other high-frequency trading brokers.
Pros | Cons |
Regulated by ASIC, FCA, CySEC, BaFin, DFSA, and CMA with segregated funds | Leverage capped at 1:30 under EU and UK entities |
Razor account offers spreads from 0.0 pips with HFT-oriented pricing | No PAMM account offering for managed allocation |
Platform range includes MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView, plus proprietary apps | Demo access can be limited depending on the region and policy |
No account keeping or inactivity fees reported by the broker | Limited bonus and promotion availability due to regulations |
TMGM
TMGM, short for TradeMax Global Markets, is an Australian broker launched in 2013 with access to 12,000+ tradable instruments across Forex, stocks, indices, metals, energies, and crypto CFDs. Traders can open CLASSIC or EDGE ECN accounts with $100 minimum deposit and base currencies like USD, AUD, EUR, GBP, NZD, and CAD.
The broker operates through several entities, led by Trademax Australia Limited under ASIC regulation with segregated funds and negative balance protection. Offshore entities regulated by VFSC, FSC Mauritius, and CMA Kenya provide higher leverage and a smooth TMGM registration process, while professional indemnity insurance coverage reaches up to AUD 10 million across jurisdictions.
For high-frequency and automated execution, TMGM highlights ECN style routing, market execution, and average execution speeds under 30 milliseconds. EDGE accounts advertise spreads from 0.0 pips with $3.5 commission per lot, and both scalping and Expert Advisors are allowed across MT4 and MT5.
TMGM expands beyond MetaTrader with IRESS for eligible stock focused traders and a proprietary mobile app for account management. TMGM dashboard provides access to copy trading and social trading are available via HUBx with ZuluTrade integration, plus a rewards program that lets active traders redeem points for cashback up to $2,500 and other incentives.
TMGM deposit and withdrawal methods include cryptocurrencies, bank cards, Neteller, Skrill, WISE, UnionPay, and many more.
Account Types | EDGE/ECN, CLASSIC |
Regulating Authorities | ASIC – Australia, VFSC – Vanuatu, CMA -Kenya, FSC-Mauritius, FSA-Seychelles |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | VISA, MasterCard, Bank Transfer, RMB Instant, Revolut, WISE, Neteller, Skrill, Union Pay, Fasapay, Crypto (USDT, USDC) |
Withdrawal Methods | Bank Transfer, RMB Instant, Revolut, WISE, Neteller, Skrill, Crypto (USDT, USDC) |
Maximum Leverage | 1:1000 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, MT5, IRESS, TMGM Mobile App |
TMGM Pros and Cons
TMGM combines deep symbol coverage, fast execution, and copy trading options, but inactivity charges and limited retail account variety can affect the overall fit. Next, the key pros and cons are listed so readers can compare TMGM with other HFT oriented brokers.
Pros | Cons |
12,000 plus tradable instruments with broad multi asset CFD coverage | Inactivity fee can apply, reported as $10 per month after extended dormancy |
ASIC-regulated primary entity with segregated funds and negative balance protection | Offshore entities are Tier 3 with lighter investor safeguards |
EDGE ECN pricing with spreads from 0.0 pips and average execution under 30ms | Retail account lineup is limited to 2 main types |
Copy trading via HUBx and ZuluTrade, plus rewards program with cashback up to $2,500 | Platform experience depends heavily on MT4 and MT5 unless using IRESS |
FP Markets
FP Markets, also known as First Prudential Markets, is an Australian broker founded in 2005 with a $50 minimum deposit and 2 core accounts, Standard and RAW. Traders can access Forex, CFDs, ETFs, indices, commodities, metals, cryptocurrencies, and stocks through MT4, MT5, and cTrader by completing the FP Markets registration process.
The broker runs a multi-entity structure regulated by ASIC and CySEC as Tier 1 authorities, alongside FSCA, CMA, FSC, and FSA jurisdictions for broader global coverage. Client safeguards include segregated funds, negative balance protection, and compensation access up to €20,000 under ICF for eligible CySEC clients.
For high-frequency and algorithmic trading, FP Markets supports RAW spreads from 0.0 pips with a $3 commission per lot and instant execution, which can suit scalping and systematic strategies. cTrader adds ECN style workflow for faster order handling, while MetaTrader enables Expert Advisors for automated execution.
FP Markets expands beyond execution with investment tools such as copy trading via its Social Trading service, plus PAMM and MAMM options for managed allocation. With base currencies ranging from USD and EUR to JPY and ZAR and maximum leverage up to 1:500 by entity, it offers flexibility for multi market portfolio setups.
Visa/Master cards, Neteller, Skrill, bank transfers, and PayPal are among the supported methods for FP Markets deposit and withdrawal.
Account Types | Standard, RAW |
Regulating Authorities | ASIC, CySEC, FSC, FSCA, FSA |
Minimum Deposit | $50 |
Deposit Methods | Visa and Master card, Skrill, PayPal, Neteller, Bank Transfer |
Withdrawal Methods | Visa and Master card, Skrill, PayPal, Neteller, Bank Transfer |
Maximum Leverage | 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, MT5, cTrader |
FP Markets Pros and Cons
The broker combines tight spreads, multi-platform execution, the FP Markets rebate program with cashbacks of up to $3/lot, and broad regulation, but limitations like no proprietary platform and regional restrictions still matter. Next, the key pros and cons are listed so readers can quickly compare FP Markets with other HFT oriented brokers.
Pros | Cons |
RAW account spreads from 0.0 pips with $3 per lot commission for cost sensitive strategies | No proprietary trading platform offered |
Tier 1 regulation via ASIC and CySEC with segregated funds and negative balance protection | Not available to US clients |
Platform choice across MT4, MT5, and cTrader for manual and automated execution | Leverage is capped at 1:30 under ASIC and CySEC entities |
Investment solutions include Social Trading, PAMM, and MAMM options | Instrument availability can vary by entity and platform |
What is High Frequency Trading?
High frequency trading, often shortened to HFT, is a form of algorithmic trading that places and cancels orders at extremely high speed. Instead of minutes or hours, many decisions happen in milliseconds or microseconds, with systems scanning prices, spreads, and news driven volatility to find tiny, repeatable edges.
HFT usually relies on low latency infrastructure, powerful hardware, and strict execution rules. The biggest performance gap often comes from distance to the broker or venue, which is why traders use VPS hosting and co location near data centers. Many brokers allow algorithmic scalping, but some prohibit latency arbitrage or similar practices.
- Executes large order volumes in very short timeframes;
- Uses algorithms to react without emotion or hesitation;
- Requires low latency connections and stable uptime;
- Works best with ECN or STP execution and tight pricing;
- Can be restricted by broker rules, message caps, or hold time limits.
Can Beginners Start with HFT Strategies?
Beginners can explore automation, but true HFT is rarely a starter skill because it depends on coding, risk management, and infrastructure. Many new traders begin with semi automated systems like Expert Advisors on MetaTrader or rule based builders like Capitalise.ai, which can introduce algorithmic thinking without institutional level speed.
If a beginner wants to move toward high-frequency styles, the safest path is building discipline first. That includes small sizing, backtesting, forward testing, and learning how spreads, commissions, and slippage change results. A broker that explicitly allows scalping and EAs matters more than marketing claims about speed.
- Start with algorithmic basics, not latency arbitrage;
- Use demo accounts and small live tests with tight risk limits;
- Track slippage, rejected orders, and fill quality;
- Avoid over leverage, especially above 1:30 for early learning;
- Confirm broker policies on scalping, EAs, and order frequency.
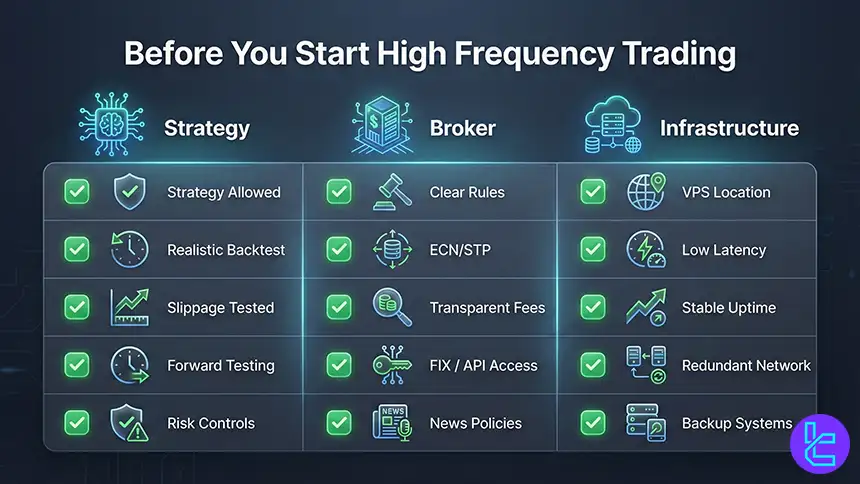
What You Need to Know Before Starting with High Frequency Trading
Before running any high-frequency strategy, understand that execution quality is part of the strategy. A profitable model in backtests can fail live due to spread expansion, slippage, and latency spikes. You need clear broker rules, a stable connection, and a plan for news events when volatility changes fill behavior.
Infrastructure choices matter as much as the algorithm. VPS hosting near the broker servers reduces network delay and improves consistency. Many serious setups also use direct connectivity such as FIX API, but access can require higher deposits and additional monthly fees depending on the broker and venue rules.
- Validate if the broker allows your exact strategy type;
- Prefer ECN or STP routing and transparent execution policies;
- Use VPS near the broker data center for consistent latency;
- Backtest with realistic costs and forward test in live conditions;
- Prepare fail safes for outages, platform freezes, and news shocks.
Best High-Frequency Trading Platform for Starters
For starters, the best platform is usually the one with the lowest friction to test ideas, manage risk, and automate safely. MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 are common entry points because they support Expert Advisors and a large ecosystem of indicators and tools. The platform cost is often included through the broker, while trading costs come from spreads and commissions.
A second beginner friendly route is code-free automation, such as Capitalise.ai, when offered by brokers like FXCM or AvaTrade. It does not match institutional HFT scale, but it can teach systematic thinking, trigger logic, and discipline. Starters should prioritize stable execution, small sizing, and repeatable monitoring.
- MetaTrader suits EA based automation and broad broker availability;
- Code free tools can simplify early automation and testing;
- Start with tight controls, small lots, and simple strategies;
- Focus on execution consistency over maximum leverage;
- Graduate to VPS once the strategy is stable and repeatable.
Algorithmic Trading in Forex
Algorithmic trading in forex uses software to place trades based on predefined rules, such as breakouts, mean reversion, or liquidity-based setups. For retail traders, this often means Expert Advisors on MetaTrader, cBots oncTrader, or custom scripts connected through broker APIs. It can operate from low timeframes, but it does not always require true HFT speed.
The practical edge comes from consistency and scalability. Algorithms can monitor many pairs, react instantly to rule triggers, and make emotional decisions. However, they also amplify mistakes if parameters are wrong. Robust backtesting, realistic cost modeling, and strict risk caps are essential, especially when spreads widen during volatile sessions.
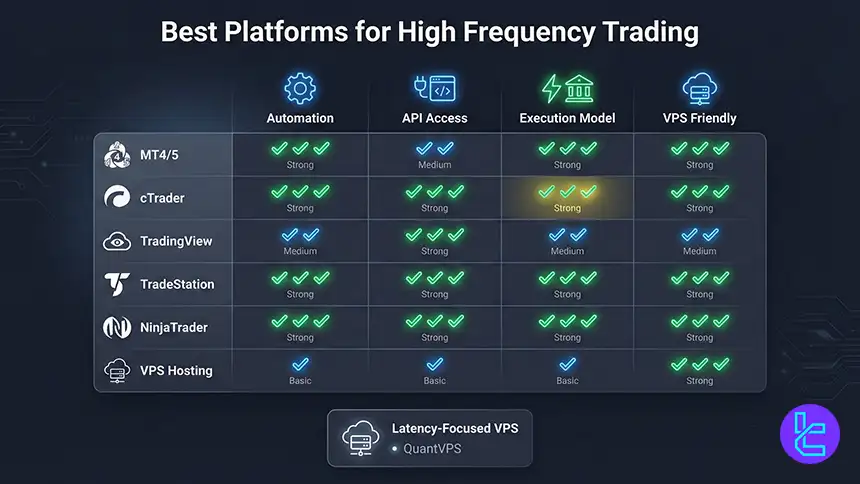
What Are the Best High-Frequency Trading Platforms?
Best platforms for high-frequency style trading usually combine automation tools, fast order handling, and flexible connectivity.
From the provided material, common choices include MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 for EA driven execution, cTrader for ECN style workflow and API use, TradingView for chart driven execution with broker integrations, and TradeStation or NinjaTrader for advanced automation ecosystems.
Infrastructure can be a platform choice too, not only software. VPS providers such as QuantVPS appear in the provided text as latency focused hosting that supports platforms like NinjaTrader, MetaTrader, and TradeStation. For brokers, IC Markets and Pepperstone are highlighted in the provided material for low spreads, strong execution focus, and platform variety.
- MetaTrader 4 and 5 for EA based automation and broad broker access
- cTrader for ECN style execution and API oriented workflows
- TradingView for charting plus broker connected execution
- TradeStation and NinjaTrader for advanced strategy development tools
- VPS hosting to stabilize latency and uptime near broker servers
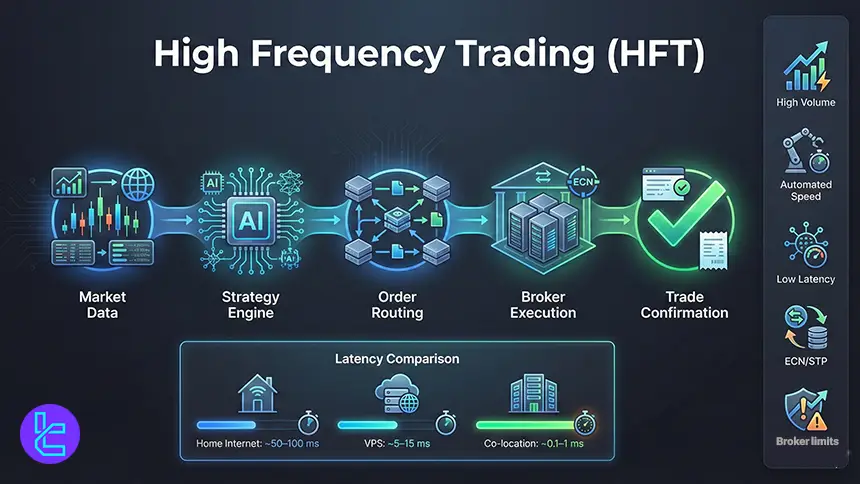
How Do HFT Platforms Work
HFT platforms are built around a loop that repeats extremely fast. First, the system reads market data, then calculates signals, then routes orders, then receives fills, and finally updates risk controls. Every step has latency, and the slowest link often defines results. Even if a trading strategy is strong, poor routing or unstable network timing can erase its edge.
Retail platforms add extra processing layers that can slow execution compared to direct protocols. That is why many HFT workflows rely on VPS hosting, co location, and sometimes FIX API connectivity, which can bypass parts of the user interface layer. Broker policies also matter, because message limits, re quotes, or hold rules can break high speed strategies.
- Data ingest, signal generation, order routing, fill confirmation loop;
- Latency comes from network, platform, broker, and liquidity routing;
- VPS improves consistency more than raw minimum ping in many cases;
- FIX API can reduce platform overhead for advanced strategies;
- Broker rules can restrict speed, order rate, or strategy types.
High Frequency Trading Advantages and Disadvantages
The biggest advantage of high-frequency trading is speed with consistency. Computers do not hesitate, and algorithms can react instantly to price changes and news driven volatility. When the execution stack is strong, HFT can capture small edges repeatedly, add liquidity, and keep decision making free from emotional errors that often harm manual traders.
The disadvantages are equally important. Algorithms can fail during abnormal conditions, and small cost changes can flip results from profit to loss. HFT also requires technical skill, infrastructure spending, and strict monitoring. Some practices like spoofing or front running are illegal, and many brokers restrict latency arbitrage or similar behavior.
- Benefits from emotion free decision making and fast reaction speed
- Can scale across symbols and sessions with consistent rules
- Sensitive to spreads, slippage, and execution instability
- Requires technical development, monitoring, and infrastructure cost
- Strategy restrictions and compliance rules can limit what is allowed

How to Choose the Best HFT Broker
Choosing an HFT broker is mostly about execution integrity and rule clarity. Look for Tier 1 regulation, segregated client funds, negative balance protection, and compensation schemes where applicable.
Next, evaluate trading conditions with your strategy in mind. ECN or STP models are often preferred for high-frequency styles because they reduce dealing desk friction. Confirm whether scalping, Expert Advisors, API trading, and high order rates are allowed. Then test slippage statistics, order types, spread behavior, and platform stability during peak sessions.
- Prefer Tier 1 regulation and clear client fund protections;
- Verify scalping, EA, API, and order frequency policies in writing;
- Compare total cost, spread plus commission, not just spread alone;
- Test execution under load during active sessions and news events;
- Ensure VPS options or data center proximity for consistent latency.
What Are the Risks of High-Frequency Trading
High-frequency trading concentrates risk into short windows, which means losses can appear quickly. Monetary risk rises when the system trades frequently, especially if leverage is high or the strategy misreads market regime changes. A small bug or wrong parameter can repeat many times before it is noticed, multiplying damage rapidly.
External and psychological risks also exist. Outages, VPS issues, data feed glitches, or broker side disruptions can cause unexpected fills or missed exits. Even if decisions are automated, the stress of rapid equity swings can be intense. The safest approach is strict max loss limits, kill switches, and routine monitoring of fills, latency, and exposure.
- Monetary risk increases with speed and repeated execution;
- Bugs and wrong parameters can multiply losses fast;
- External risk includes outages, feed errors, and platform freezes;
- Psychological strain can grow from rapid peaks and drawdowns;
- Risk controls need kill switches, max loss caps, and monitoring.
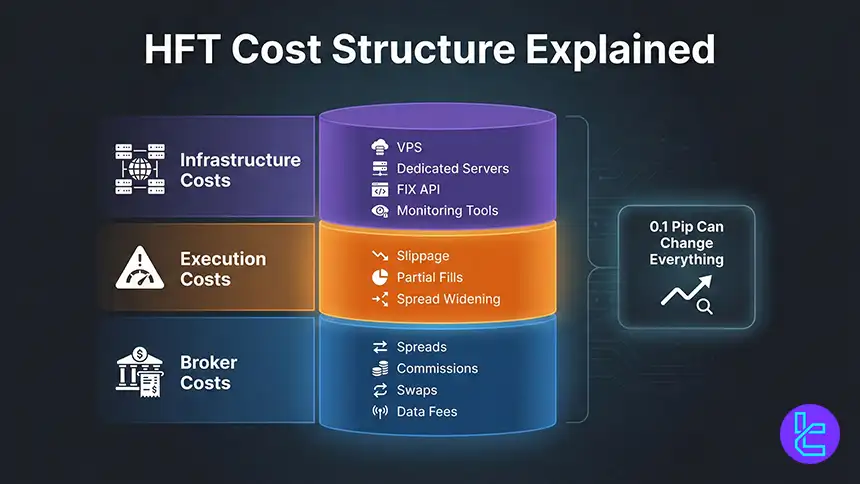
What Costs Are Associated with High-Frequency Trading?
HFT costs include visible fees and hidden execution costs. Visible costs are spreads, commissions, swaps, and sometimes platform or data subscriptions.
Hidden costs come from slippage, partial fills, and spread widening during volatility. For high-frequency systems, even a 0.1 pip difference can change the profit curve because the strategy repeats so often.
Infrastructure costs are common once you move beyond basic automation. VPS, dedicated server pricing, and FIX API access may involve monthly connectivity fees and higher minimum deposits. Budgeting should include VPS, data, platform tools, development time, and monitoring, not only trading fees.
VPS and Co-Location for High-Frequency Trading
VPS hosting is often the minimum standard for any serious high-frequency style strategy because it reduces routing distance and stabilizes latency. Home networks can fluctuate heavily, and small spikes can ruin entries and exits. A VPS near the broker servers improves consistency, which is often more valuable than achieving the absolute lowest ping once.
Co-location is the next step, placing your trading server in the same data center as the broker or venue. Equinix locations such as NY4, LD4, and TY3 are common hubs for liquidity and broker infrastructure. Not every retail trader needs co-location, but it becomes important for latency-sensitive models.
HFT Platforms Comparison Table
The table below compares common HFT-relevant platforms and stacks. Latency is often broker-dependent for retail platforms, while VPS solutions focus on reducing network delay and stabilizing uptime. Use this as a starting point, then validate with live tests on your broker and VPS location.
Platform or stack | Typical latency | Automation or API | Cost model | Best for | Main limitation |
MetaTrader 4 and 5 | Broker dependent | MQL4 or MQL5 EAs | Broker pricing | EA based automation for forex and CFDs | Not purpose built for institutional HFT |
cTrader | Broker dependent, often low on ECN brokers | cTrader API and FIX on some brokers | Broker pricing | ECN style execution and algo workflows | Availability varies by broker |
TradingView connected brokers | Broker dependent | Alerts and broker integrations | Subscription plus broker costs | Chart driven execution and monitoring | Not a native HFT engine |
TradeStation | Fast execution | EasyLanguage and APIs | Commissions plus data | Advanced development for active traders | Higher data and account requirements |
NinjaTrader | Sub second routing | C# automation and interfaces | License or subscription | Futures and advanced automation | Windows focused ecosystem |
VPS hosting, such as QuantVPS | Can reduce to under 1ms depending on location | Platform dependent | Monthly hosting | Stabilizing latency and uptime | Not a trading platform by itself |
Conclusion and Final Words
High-frequency trading platforms succeed only when technology, pricing, and broker infrastructure work in perfect alignment. Sub-50ms execution, FIX API connectivity, VPS hosting, and ECN routing remain essential for managing thousands of orders per second.
Beyond raw speed, long-term HFT success depends on regulatory reliability, transparent cost structures, and access to diversified instruments. Trustpilot ratings, minimum spreads, non-trading fees, and asset coverage reveal how brokers balance performance with client satisfaction.
All broker evaluations in this guide are based on the TradingFinder Forex Methodology, which analyzes regulation, execution quality, pricing models, platform stability, infrastructure access, and real trader feedback.













